Why?
We will store transformations to correctly position and align 3D models in space.
To align two 3D models correctly using their transformation matrices, you need to understand how to manipulate these matrices mathematically. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the process:
Understanding Transformation Matrices
A transformation matrix in 3D space is typically represented as a 4x4 matrix in homogeneous coordinates. This matrix can encapsulate various transformations such as translation, rotation, and scaling. The general form of a transformation matrix MM is:
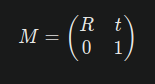
Where:
- R is a 3x3 rotation matrix.
- t is a 3x1 translation vector.
- The last row is always (0,0,0,1)(0,0,0,1) to maintain the homogeneous coordinate system.
Steps to Align Two Models
- Extract Transformation Matrices: Assume you have two models with their respective transformation matrices M1 and M2.
- Compute the Inverse of the First Model's Matrix: To align model 2 with model 1, you need to compute the inverse of M1:
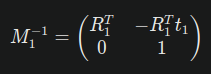
Where is the transpose of the rotation matrix (which serves as its inverse for orthogonal matrices), and translates the origin back to the first model's position. - Transform the Second Model: Multiply the inverse of the first model's transformation matrix by the second model's transformation matrix:
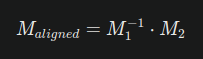
This operation aligns model 2 with respect to model 1’s coordinate system. - Apply the Aligned Transformation: The resulting matrix
can now be used to transform the vertices of model 2 into the coordinate space of model 1.
Example Calculation
If you have specific matrices, for example:
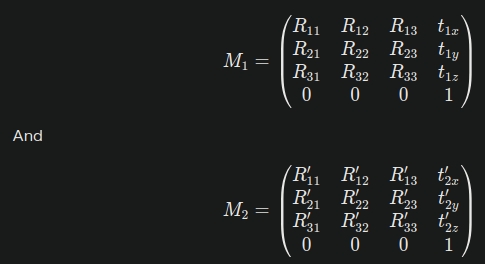
You would compute M1−1M1−1 and then perform the multiplication to find